7.1 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (easy)
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:
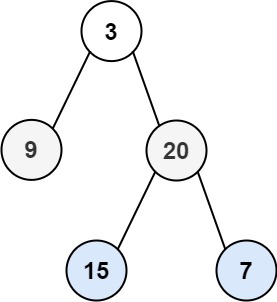
Example 2:
Example 3:
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000].-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Time complexity #
The time complexity of the above algorithm is O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the tree. This is due to the fact that we traverse each node once.
Space complexity #
The space complexity of the above algorithm will be O(N) as we need to return a list containing the level order traversal. We will also need O(N) space for the queue. Since we can have a maximum of N/2 nodes at any level (this could happen only at the lowest level), therefore we will need O(N) space to store them in the queue.
Last updated