7.6 Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (easy)
Last updated

Last updated
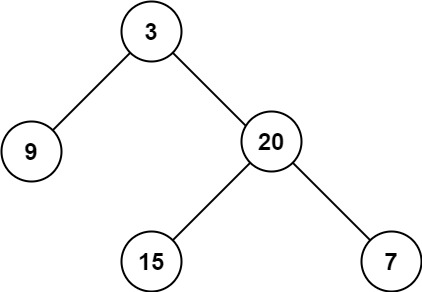
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2import java.util.*;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
};
class Main {
public static int findDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int maximumTreeDepth = 0;
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
maximumTreeDepth++;
int levelSize = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode currNode = queue.poll();
if(currNode.left != null) queue.offer(currNode.left);
if(currNode.right != null) queue.offer(currNode.right);
}
}
return maximumTreeDepth;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(12);
root.left = new TreeNode(7);
root.right = new TreeNode(1);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(10);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(5);
System.out.println("Tree Maximum Depth: " + Main.findDepth(root));
root.left.left = new TreeNode(9);
root.right.left.left = new TreeNode(11);
System.out.println("Tree Maximum Depth: " + Main.findDepth(root));
}
}